Unlocking Restful Nights: Your Guide to Relaxation for Better Sleep
Are you tired of tossing and turning? Do racing thoughts keep you awake at night? Quality sleep is essential for well-being, yet many struggle to achieve it. This article presents eight effective relaxation techniques for better sleep, providing actionable strategies to improve your sleep quality. We'll explore practical methods to calm your mind and body, paving the way for restful nights and energized days.
Struggling with insomnia, snoring, shift work, or jet lag? These relaxation techniques offer solutions tailored to various sleep challenges. Learn how to incorporate these practices into your routine and experience the transformative power of deep, restorative sleep.
This listicle provides clear, step-by-step instructions for each technique, ensuring you can implement them easily. Discover how practices like progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and mindfulness can help you unwind before bed and finally get the sleep you deserve. We'll explore the science behind these relaxation techniques and provide practical tips for maximizing their effectiveness. Explore this curated collection and find the perfect relaxation method to transform your sleep.
1. Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) is a powerful relaxation technique developed by physician Edmund Jacobson in the 1920s. It involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body. This process helps differentiate between tension and relaxation, reducing physical tension and anxiety for better sleep. PMR is a valuable tool for anyone seeking deeper, more restful sleep as it addresses the physical manifestations of stress that often disrupt sleep.
How PMR Works
PMR works on the principle that physical relaxation can lead to mental calmness. By tensing a muscle group, you bring heightened awareness to that specific area. The subsequent release of tension creates a noticeable sensation of relaxation. This conscious act of tensing and relaxing trains your body to recognize and release tension, promoting a state conducive to sleep.
Examples of PMR in Practice
PMR's effectiveness has led to its integration into various therapeutic settings:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): PMR is a core component of CBT-I programs, helping individuals manage racing thoughts and physical tension that prevent sleep.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): PMR complements mindfulness practices, enhancing body awareness and promoting overall relaxation.
- Hospital Settings: PMR helps reduce pre-surgical anxiety and promotes relaxation during recovery. It is also valuable in the broader population where stress and anxiety contribute to poor sleep, and has also been integrated into modern sleep applications such as Headspace and Calm.
Practical Tips for Using PMR
- Short on Time? Focus on major muscle groups like shoulders, arms, and legs for a quicker relaxation exercise.
- Set the Scene: Practice PMR in a quiet, dimly lit room before bedtime to create a sleep-inducing environment.
- Guided Assistance: Use audio recordings initially to guide you through the proper technique and timing.
- Notice the Contrast: Pay close attention to the sensations of tension and relaxation to enhance your body's awareness.
- Gentle Tensing: Avoid excessive muscle tension to prevent cramping; focus on a noticeable but comfortable level of tension.
The following infographic details the basic three-step process involved in Progressive Muscle Relaxation.
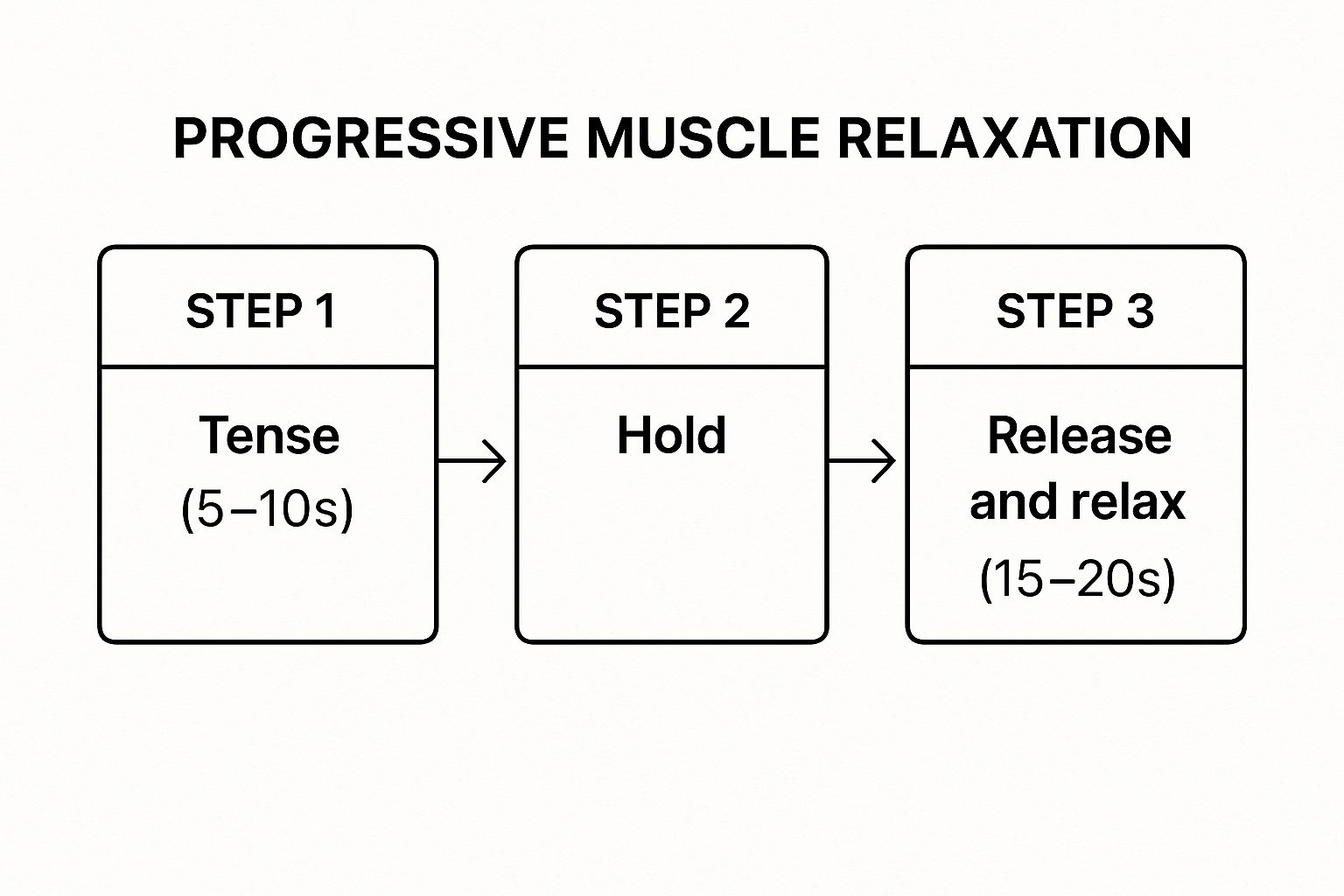
The infographic illustrates the core PMR process: tensing a muscle group for 5-10 seconds, holding the tension briefly, and then releasing and relaxing for 15-20 seconds. This cyclical process allows the body to experience and recognize the difference between tension and relaxation, a key aspect of successful PMR.
PMR is a simple yet highly effective relaxation technique for better sleep. By incorporating PMR into your bedtime routine, you can actively reduce physical tension, quiet the mind, and create a more conducive environment for restful sleep. Its versatility and adaptability make it suitable for individuals struggling with various sleep challenges, from insomnia to racing thoughts.
2. Deep Breathing Exercises (Diaphragmatic Breathing)
Deep breathing exercises, specifically diaphragmatic breathing, are a fundamental relaxation technique for better sleep. Unlike shallow chest breathing, this practice engages the diaphragm, allowing for deeper, more effective respiration. This activates the parasympathetic nervous system, effectively lowering heart rate and blood pressure to promote a state of calm conducive to sleep. It's one of the most accessible and readily available relaxation techniques.
How Diaphragmatic Breathing Works
Diaphragmatic breathing works by encouraging full lung capacity. As you inhale deeply, the diaphragm contracts and moves downwards, allowing the lungs to expand fully. This intake maximizes oxygen delivery. Upon exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and moves upwards, expelling carbon dioxide and promoting relaxation. This rhythmic process helps regulate the body's natural relaxation response.
Examples of Diaphragmatic Breathing in Practice
Several established techniques utilize diaphragmatic breathing:
- 4-7-8 Breathing: Popularized by Dr. Andrew Weil, this technique involves inhaling for a count of 4, holding for 7, and exhaling for 8. It is known for its quick relaxation benefits.
- Box Breathing: Used by Navy SEALs for stress management, this method involves inhaling, holding, exhaling, and holding again, each for a count of 4, visualizing a box.
- Pranayama: Various yogic breathing practices focus on controlled diaphragmatic breathing to regulate energy and promote relaxation.
- Meditation and Sleep Apps: Deep breathing exercises are integrated into numerous apps like Headspace and Calm, demonstrating their widespread use for relaxation and sleep improvement.
Practical Tips for Using Diaphragmatic Breathing
- Hand Placement: Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly. As you breathe, ensure only your belly moves, confirming diaphragmatic engagement.
- Counting Breaths: Start with a simple 4-4-6 count - inhale for 4, hold for 4, exhale for 6. Gradually increase the exhale length for enhanced relaxation.
- Daytime Practice: Practice throughout the day to make nighttime use more natural and effective.
- Focus on Exhales: Longer exhales compared to inhales maximize the relaxation response.
- Start Small: Begin with 5-10 minutes of practice and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable.
Deep breathing is a simple, yet powerful relaxation technique for better sleep. By incorporating these exercises into your daily routine, and especially before bed, you can effectively manage stress, lower anxiety, and promote a state of relaxation conducive to restful, restorative sleep. Its accessibility and ease of use make it an ideal starting point for anyone seeking improved sleep quality.
3. Guided Imagery and Visualization
Guided imagery and visualization is a powerful mental relaxation technique that uses the power of imagination to promote calmness and improve sleep. It involves creating detailed, peaceful mental images to distract from stressful thoughts and prepare the body for rest. This method effectively reduces anxiety and promotes relaxation by shifting focus away from daily concerns and physical discomfort. By transporting the mind to tranquil settings, guided imagery helps create a mental state conducive to sleep.

How Guided Imagery Works
Guided imagery harnesses the mind-body connection. When you vividly imagine a peaceful scene, your body responds as if you were actually there. This can lead to physiological changes such as slowed breathing, reduced heart rate, and decreased muscle tension, all of which contribute to a state of relaxation ideal for sleep. By consistently practicing guided imagery, you can train your mind to access this relaxed state more readily at bedtime.
Examples of Guided Imagery in Practice
The versatility of guided imagery allows for a wide range of applications:
- Nature Scenes: Imagine strolling through a serene forest, feeling the soft earth beneath your feet and listening to the gentle rustling of leaves.
- Water Settings: Visualize floating on calm water under a starlit sky, feeling the gentle rocking motion and the cool breeze on your skin.
- Body Scan Meditations: Combine guided imagery with a mental body scan, imagining warm, healing light flowing through your body, releasing tension in each area.
- Sleep Stories: Utilize guided sleep stories, readily available in apps like Calm, Insight Timer, and Sleep Stories, which often incorporate calming narratives and soothing soundscapes.
Practical Tips for Using Guided Imagery
- Personal Resonance: Choose imagery that personally resonates with you and evokes a sense of peace and safety.
- Sensory Engagement: Engage all five senses in your visualizations to create a more immersive and relaxing experience.
- Repetition: Practice the same imagery repeatedly to strengthen the relaxation response and make it easier to access before sleep.
- Descriptive Language: Use slow, descriptive language when self-guiding to enhance the vividness of your mental images.
- Sound Integration: Combine guided imagery with soft background sounds or white noise to create a more tranquil environment.
Guided imagery and visualization is a simple yet effective relaxation technique for better sleep. By incorporating this practice into your bedtime routine, you can actively calm your mind, reduce stress, and create a mental sanctuary that promotes restful, restorative sleep. Its accessibility and adaptability make it a valuable tool for anyone seeking to improve their sleep quality through the power of imagination.
4. Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation, a practice rooted in Buddhist tradition, involves cultivating moment-to-moment awareness of thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations without judgment. For better sleep, this technique helps break the cycle of rumination and anxiety that often prevents sleep onset. It teaches practitioners to observe their thoughts without becoming entangled in them, fostering a sense of calm conducive to sleep. This makes it a valuable tool in addressing the mental aspects that frequently disrupt sleep.
How Mindfulness Meditation Works
Mindfulness meditation works by shifting the focus from racing thoughts to present-moment experiences. By anchoring attention to the breath or body sensations, you create a point of focus that gently redirects the mind away from worries and anxieties. This redirection helps quiet the internal chatter, allowing the body and mind to relax and prepare for sleep. Consistent practice strengthens this ability to disengage from stressful thoughts, promoting more restful sleep.
Examples of Mindfulness Meditation in Practice
Mindfulness meditation has gained widespread recognition for its effectiveness, leading to its integration into various settings:
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): 8-week programs provide structured training in mindfulness meditation for stress management and overall well-being.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): This approach integrates mindfulness meditation with cognitive therapy techniques to address depression and anxiety, which often contribute to sleep disturbances.
- Corporate Wellness Programs: Companies like Google and Apple offer mindfulness programs to employees, recognizing the benefits for stress reduction and improved focus.
- Healthcare Systems: Mindfulness meditation is increasingly integrated into healthcare for managing chronic pain and insomnia.
Practical Tips for Using Mindfulness Meditation
- Start Small: Begin with just 5-10 minutes of meditation before bed.
- Anchor Your Attention: Focus on your breath or body sensations as anchor points to bring you back to the present moment.
- Be Kind to Yourself: When your mind wanders, gently redirect your attention without self-criticism.
- Guided Assistance: Use apps like Headspace, Insight Timer, or Ten Percent Happier for guided meditations.
- Daytime Practice: Practicing mindfulness during the day strengthens your skills for nighttime use.
Learn more about Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation provides a simple yet effective way to address the mental barriers to restful sleep. By incorporating this technique into your bedtime routine, you can quiet the mind, reduce anxiety, and create a more conducive environment for deep, restorative sleep. Its accessibility and adaptability make it a valuable tool for anyone seeking relaxation techniques for better sleep.
5. Body Scan Meditation
Body Scan Meditation is a systematic mindfulness practice that involves mentally scanning through different parts of the body, from head to toe. It encourages gentle awareness of physical sensations, tension, or areas of relaxation without judgment. This technique combines elements of mindfulness with physical awareness, helping to release physical tension and calm the mind for better sleep. Body Scan Meditation is a valuable tool for those seeking relaxation techniques for better sleep as it addresses both physical and mental barriers to rest.
How Body Scan Meditation Works
Body Scan Meditation works by bringing focused attention to each part of the body. This heightened awareness allows you to notice and acknowledge physical sensations without trying to change them. The practice cultivates a sense of acceptance and non-judgmental observation, which helps reduce the tendency to react to discomfort or pain. This, in turn, promotes relaxation and reduces the mental chatter that can interfere with sleep.
Examples of Body Scan Meditation in Practice
The versatility of Body Scan Meditation has led to its widespread adoption:
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): Body Scan Meditation is a core practice in MBSR programs, helping participants develop body awareness and manage stress.
- Yoga Nidra: This "yogic sleep" practice incorporates Body Scan Meditation to induce deep relaxation and a state of conscious rest.
- Chronic Pain Management: Body Scan Meditation helps individuals cope with chronic pain by shifting their relationship to physical sensations.
- Meditation Apps: Guided Body Scan Meditations are readily available on most meditation apps, making the practice accessible to a wider audience.
Practical Tips for Using Body Scan Meditation
- Systematic Approach: Start at the top of your head and systematically move your attention down through each body part.
- Time Commitment: Spend 30-60 seconds noticing each area, observing any sensations without judgment.
- Acceptance is Key: Don't try to force relaxation; simply observe what's already present.
- Gentle Curiosity: Approach the practice with a sense of gentle curiosity, rather than forcing awareness.
- Holistic Awareness: End the practice by noticing the body as a whole, interconnected system.
Body Scan Meditation is a powerful yet gentle relaxation technique for better sleep. By incorporating this practice into your routine, you can cultivate body awareness, release physical tension, and quiet the mind, creating a more conducive environment for restful sleep. Its accessibility and adaptability make it a valuable tool for anyone seeking deeper, more restorative sleep.
6. Autogenic Training
Autogenic Training (AT) is a self-hypnosis relaxation technique developed by German psychiatrist Johannes Schultz in the 1930s. It involves using specific verbal formulas to induce physical sensations of warmth and heaviness, promoting deep relaxation and improved sleep. This systematic approach teaches the body to relax on command, making it a valuable tool for managing stress and preparing for restful sleep. AT addresses the mental and physical components of relaxation, offering a powerful technique for those seeking better sleep.
How Autogenic Training Works
Autogenic Training works by leveraging the mind-body connection. Repeating specific phrases focused on warmth and heaviness creates corresponding physiological changes in the body. This process reduces activity in the sympathetic nervous system (responsible for the "fight-or-flight" response) and activates the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress hormones. The consistent practice of AT enhances the body's ability to relax deeply, facilitating the transition into sleep.
Examples of Autogenic Training in Practice
Autogenic Training's effectiveness has led to its adoption in various settings:
- European Healthcare Systems: AT is commonly used for stress management and anxiety reduction within European healthcare.
- Sports Psychology: Athletes utilize AT to manage performance anxiety and enhance focus.
- Corporate Wellness Programs: AT is integrated into corporate wellness programs to help employees cope with workplace stress.
- Specialized Relaxation and Sleep Clinics: Clinics specializing in relaxation and sleep often incorporate AT as a core therapeutic technique.
Practical Tips for Using Autogenic Training
- Consistent Formulas: Practice the same verbal formulas consistently for optimal results. Start with "My right arm is heavy" and progress systematically through the body.
- Passive Concentration: Don't force sensations; allow them to develop naturally through passive concentration.
- Regular Practice: Practice twice daily (morning and evening) for the best results and to reinforce the relaxation response.
- Natural Progression: Start with basic exercises focusing on heaviness and warmth, and gradually progress to more complex visualizations as you become proficient.
- Patience is Key: Autogenic Training requires patience and regular practice to experience its full benefits.
Autogenic Training is a highly effective relaxation technique for better sleep. By incorporating AT into your daily routine, you can train your body to relax deeply, reduce stress, and prepare for more restful sleep. Its focus on self-regulation and the mind-body connection empowers individuals to manage their own relaxation response, leading to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
7. Yoga Nidra (Yogic Sleep)
Yoga Nidra, often called "yogic sleep," is an ancient practice that guides practitioners into a state of conscious deep relaxation between waking and sleeping. This systematic meditation technique combines body awareness, breath work, and visualization to induce profound relaxation. Uniquely, it maintains a thread of consciousness, making it ideal for transitioning into natural sleep and improving sleep quality. Yoga Nidra addresses the mental and emotional tension that often prevents restful sleep.
How Yoga Nidra Works
Yoga Nidra works by systematically moving your attention through different parts of the body, breath, sensations, emotions, and visualizations. This process calms the nervous system, releases muscular tension, and stills the mind. By maintaining awareness throughout the practice, you can experience deep relaxation without falling into unconscious sleep, though doing so is perfectly acceptable and still beneficial. This conscious relaxation is key to unlocking deeper, more restorative sleep.
Examples of Yoga Nidra in Practice
Yoga Nidra's effectiveness has led to its widespread adoption in various settings:
- Yoga Studios and Meditation Centers: Yoga Nidra is commonly offered as a standalone class or incorporated into existing yoga and meditation programs.
- Trauma Therapy: Its ability to induce deep relaxation makes it a valuable tool in trauma therapy and PTSD treatment, helping individuals process trauma and manage associated sleep disturbances.
- Wellness Retreats: Yoga Nidra is often featured in wellness retreats and stress management programs to promote relaxation and rejuvenation.
- Specialized Apps: The growing popularity of Yoga Nidra has led to its inclusion in dedicated apps like the Yoga Nidra Network, making the practice accessible anytime, anywhere.
Practical Tips for Using Yoga Nidra
- Comfortable Environment: Practice in a warm, comfortable space with minimal distractions.
- Set an Intention (Sankalpa): At the beginning of the practice, set a positive intention or affirmation to focus your mind and enhance the practice's benefits.
- Guided Instructions: Follow guided instructions without trying to control the experience. Let go and allow the practice to unfold naturally.
- Embrace Sleep: It's perfectly okay to fall asleep during Yoga Nidra. The practice still provides benefits even if you drift off.
- Regular Practice: For best results, practice Yoga Nidra regularly, preferably at the same time each day, to establish a consistent routine.
Learn more about stress relief and relaxation techniques through yoga poses from this resource: Learn more about...
Yoga Nidra is a powerful relaxation technique for better sleep. By incorporating it into your routine, you can access deep relaxation, reduce stress, and prepare your mind and body for restful, restorative sleep. Its unique blend of conscious relaxation and guided meditation makes it a valuable tool for anyone seeking to improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.
8. White Noise and Sound Therapy
White noise and sound therapy utilize consistent, soothing sounds to mask disruptive noises and promote relaxation for better sleep. This technique provides a constant auditory backdrop, helping the brain filter out sudden noises that can cause awakenings. It creates a calming atmosphere conducive to both sleep onset and maintenance. This makes it a valuable tool for anyone seeking deeper, more restful sleep, especially in noisy environments or for those with heightened sensitivity to sound.

How Sound Therapy Works
Sound therapy for sleep relies on the principle of auditory masking. Consistent sounds like white, pink, or brown noise, or natural sounds like rain or ocean waves, cover up jarring noises that might otherwise disturb sleep. This constant sound creates a more peaceful sleep environment, reducing the likelihood of being startled awake. It also promotes relaxation by providing a gentle, soothing auditory focus.
Examples of Sound Therapy in Practice
Sound therapy has found applications in various settings:
- Hospitals and Sleep Clinics: White noise machines are frequently used to mask hospital noises and promote patient sleep.
- Sleep Apps: Numerous apps offer a variety of nature sounds, white noise, and even ASMR recordings specifically designed for sleep.
- Home Use: White noise machines and nature sound apps help people create peaceful sleep environments in their own bedrooms.
Practical Tips for Using Sound Therapy
- Experiment with Sounds: Explore different types of sounds, from white and pink noise to nature sounds and ASMR, to find what works best for you. Learn more about...
- Volume Control: Keep the volume at a comfortable level, not too loud or too soft. It should be noticeable enough to mask disruptive noises but not so loud that it becomes a distraction itself.
- Timer Option: If you prefer not to have sound playing all night, use a timer function to automatically turn it off after a set period.
- Combination Therapy: Combine sound therapy with other relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation, for enhanced effectiveness.
- Partner Consideration: If sharing a bed, consider using earbuds or sleep headphones to avoid disturbing your partner.
White noise and sound therapy offer a simple yet effective way to improve sleep quality by creating a more peaceful and relaxing sleep environment. Its accessibility through various apps and devices makes it a practical solution for individuals seeking better sleep in today's often noisy world.
Relaxation Techniques Comparison Matrix
| Technique | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) | Moderate (systematic muscle engagement) | Low (no equipment) | Reduces physical tension and anxiety; improves sleep quality | Physical tension, anxiety-related insomnia, pain management | Scientifically proven; improves body awareness; structured approach |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Low (simple breathing patterns) | None | Immediate calming effect; lowers heart rate and blood pressure | Beginners; people with racing thoughts; immediate stress relief | Accessible anytime; no cost; suitable for all ages |
| Guided Imagery and Visualization | Low to moderate (mental imagery focus) | None or audio support | Reduces anxiety; mental distraction from stress; improves focus | Visual learners; people with racing minds; creative types | Personalized; mental escape; enhances focus and sleep association |
| Mindfulness Meditation | Moderate (requires practice) | None or app guidance | Reduces rumination and worry; long-term mental health benefits | Anxiety, depression, chronic pain; long-term improvement | Backed by extensive research; broad mental health benefits |
| Body Scan Meditation | Moderate (systematic body focus) | None or guided audio | Releases physical tension; calms mind for sleep | Physical tension; structured meditation seekers | Combines mindfulness with physical relaxation; can be done lying down |
| Autogenic Training | Moderate to high (verbal formulas) | None | Physical sensations of warmth/heaviness; self-induced relaxation | Structured approach seekers; anxiety disorders; self-hypnosis | Highly structured; extensive research support; independent practice |
| Yoga Nidra (Yogic Sleep) | Moderate to high (guided practice) | Guided recordings or instructor | Deep relaxation; restorative benefits similar to sleep | Yoga practitioners; trauma histories; those seeking deep restoration | Extremely effective; addresses physical and psychological aspects |
| White Noise and Sound Therapy | Low (simple setup) | White noise machines or apps | Masks environmental noise; improves sleep maintenance | Light sleepers; noisy environments; shift workers | Immediate effect; wide sound options; inexpensive and accessible |
Sweet Dreams: Putting Relaxation into Practice
Mastering relaxation techniques is a powerful investment in your sleep quality and overall well-being. From the structured approach of Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) to the simplicity of deep breathing exercises, the techniques discussed in this article offer a diverse toolkit for combating sleep challenges. The key is to find what resonates with you and integrate it consistently into your pre-sleep routine.
Key Takeaways for Better Sleep
Let's recap the essential takeaways to help you implement these relaxation techniques for better sleep:
- Consistency is Key: Practicing these techniques regularly, even for short periods, is more effective than sporadic attempts.
- Personalization Matters: Experiment with different techniques to discover what works best for your individual needs and preferences.
- Create a Sleep Sanctuary: Optimizing your sleep environment is crucial. This includes factors like temperature, lighting, and noise levels.
- Mind-Body Connection: Relaxation techniques harness the power of the mind-body connection to promote calmness and prepare you for restful sleep.
Taking the Next Steps Towards Tranquility
Improving your sleep isn't just about counting sheep; it's about actively cultivating a state of relaxation. By integrating these techniques into your life, you're not merely addressing sleep issues but embracing a holistic approach to well-being. Consider keeping a sleep journal to track your progress and identify patterns that contribute to or hinder your sleep quality. Note how different relaxation techniques impact your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
The Power of a Peaceful Night's Rest
Quality sleep is the foundation of a healthy and productive life. It enhances cognitive function, boosts mood, strengthens the immune system, and improves overall physical health. By prioritizing relaxation techniques, you're prioritizing these vital benefits. Remember, consistent effort is crucial. The more you practice, the more proficient you'll become at achieving a deep state of relaxation conducive to sound sleep.
Enhancing Relaxation with Aloha Relax
Imagine combining the power of these relaxation techniques with a sleep environment optimized for tranquility. Aloha Relax offers products designed to enhance your sleep experience, such as their innovative 3D Bluetooth sleep masks, perfect for incorporating sound therapy or guided meditation into your routine. Visit Aloha Relax and discover how their products can further elevate your relaxation practices and help you achieve truly restful sleep.

